Project overview
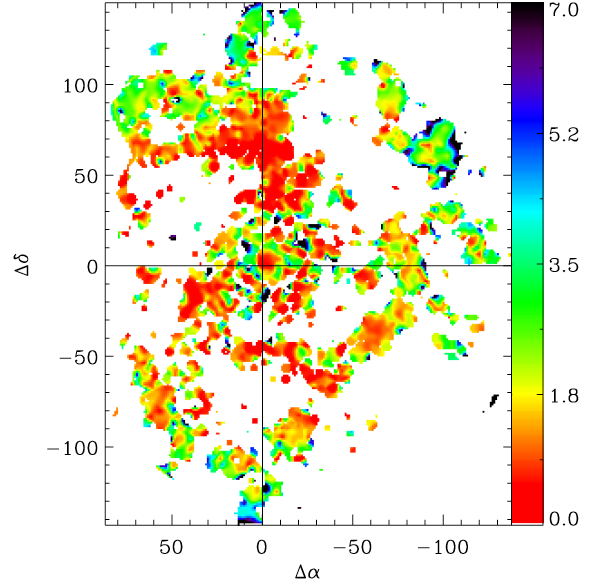
The PPAK IFS Nearby Galaxies Survey (PINGS) is a
2-dimensional spectroscopic mosaicking of 17 nearby disk
galaxies in the optical wavelength range. This project
represented the first attempt to obtain continuous
coverage spectra of the whole surface of a galaxy in the
nearby universe using the instrumental capabilities of
the PMAS/PPAK spectrograph at the
Centro Astronómico Hispano-Alemán at Calar Alto, Spain. For more
details on the project and related science see the
Publications section.
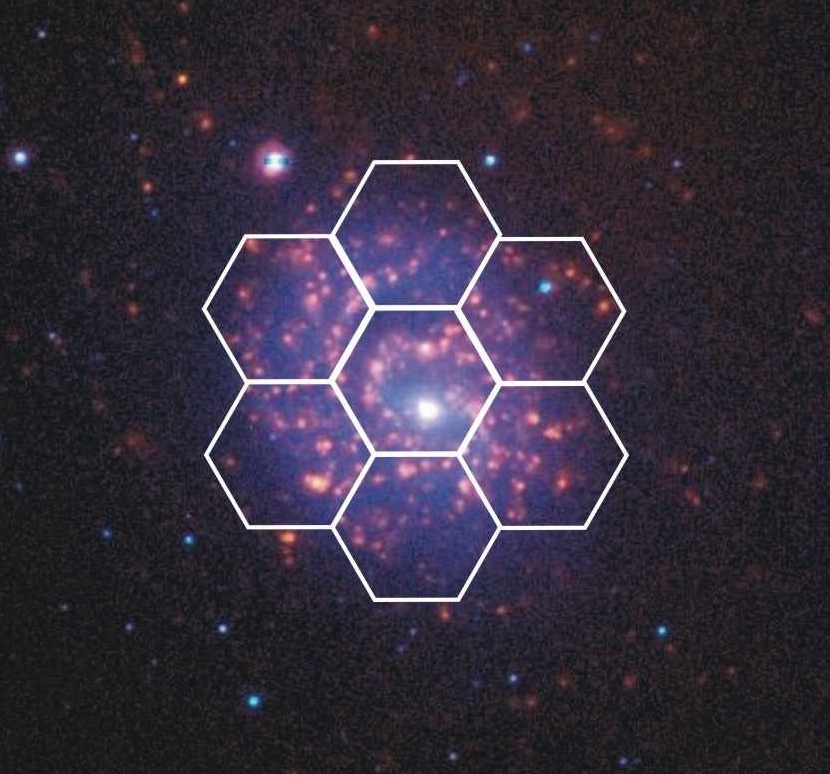

The instrument
The PMAS/PPAK instrument is one of the
world's widest integral field unit (IFU) which
provides a semi-contiguous regular sampling of
extended astronomical objects (~ 1.25 arcmin). The
Postdam
Multi-Aperture
Spectrophotometer
(PMAS) is a dedicated integral field spectrophotometer
optimised to cover the optical wavelength regime of
0.35-1 microns. It is based on a lens array-fiber bundle
principle of operation. The PMAS fiber
PAcK (PPAK) is a
retrofitted bare fiber bundle IFU which expands the FOV
of PMAS to an hexagonal area with a footprint of 65 x 74
arcsec. The PPAK unit features a central hexagonal bundle
with 331 densely packed optical fibers to sample an
astronomical object at 2.7 arcsec per fiber. A single
large PPAK fiber collects more light even with a 3.5
telescope than a single spatial element of an IFU mounted
in a 8m-class telescope. PPAK is ideally suited to study
extended astronomical objects with low surface
brightness, where light collecting power is more
important than detailed spatial resolution.
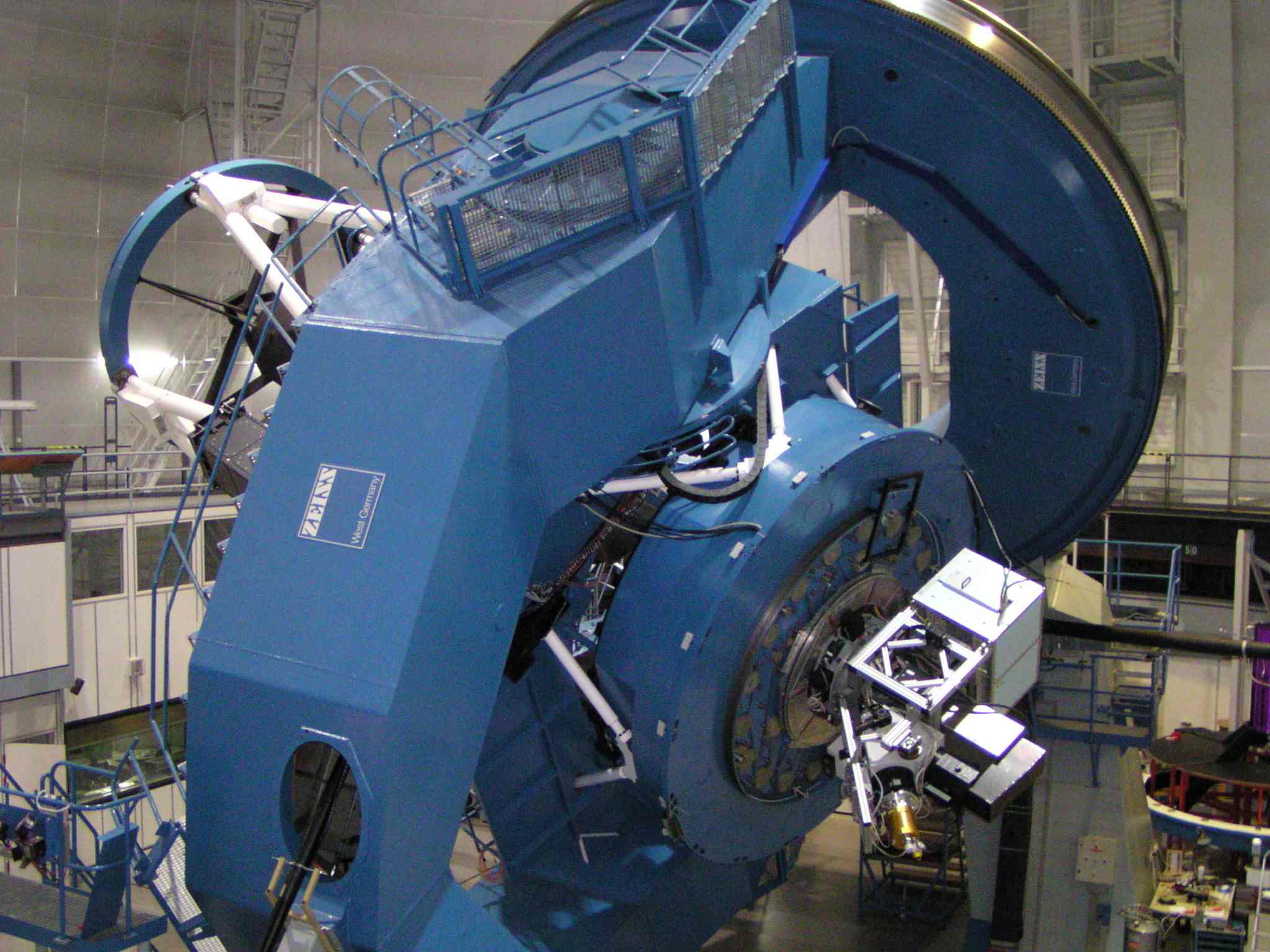

Left: PMAS-PPAK mounted at 3.5m telescope at
CAHA.
Right: PPAK-IFU diagram, showing the hexagonal
field of view of the instrument.